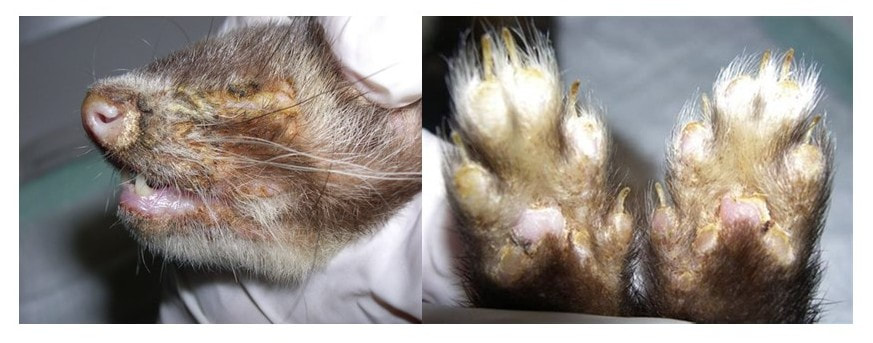
Canine Distemper Vaccines - Approved for use in Ferrets:
As of March 2021, two USDA-licensed CDV vaccines are available for administration by a licensed veterinarian:
NeoVac FD [modified live virus]
Purevax DV-Ferret [modified live virus] [live canarypox vector]
As of March 2021, two USDA-licensed CDV vaccines are available for administration by a licensed veterinarian:
NeoVac FD [modified live virus]
- Manufacturer: NeoTech, LLC, Dresden, TN-USA
- US Vet License No. 472 T: 1-877-636-8324 company website: www.neovacfd.com
- Dosing: Safe in ferrets 6 weeks of age and older. Recommend primary vaccination at 8 weeks and 1 additional dose 3 weeks later. Revaccinate annually with a single dose.
- Store unreconstituted: 2-7°C (35-45°F). Gentamicin used as preservative.
- Precautions: Do not vaccinate if animal is pregnant, lactating, or is sick or debilitated.
- Potential adverse events: May cause allergic reactions, including severe (anaphylaxis). Treatment directed by a veterinarian
Purevax DV-Ferret [modified live virus] [live canarypox vector]
- Manufacturer: Merial, Ltd. (Duluth, GA- USA), distributed by Behringer Ingelheim Animal Health Canada Inc, Burlington, Ontario, Canada
- US Vet License No. 298 T: 1-888-637-4251 [no company website available]
- Dosing: Healthy ferrets 8 weeks of age and older. Primary vaccination requires 2 additional doses at 3 week intervals. Revaccinate annually with a single dose.
- Store unreconstituted: 2-7°C (35-45°F). Gentamicin used as preservative.
- Precautions: It is generally recommended to avoid vaccination of pregnant ferrets.
- Potential adverse events: May cause lethargy, fever, and inflammatory or hypersensitivity types of reactions. Transient lethargy, as well as pain and swelling at the site of injection. Treatment may include antihistamines, anti-inflammatories, and/or epinephrine, as directed by a veterinarian.
RABIES VIRUS VACCINE
Rabies ("madness") is a viral infection that causes acute inflammation of the brain ("encephalitis"). The Rabies Virus travels through peripheral nervces to the central nervous system, infecting brain cells, creating "negri" (black) bodies that are detected on pathological examination of the brain. Once an animal is showing signs of Rabies, the outcome is usually fatal.
All warm-blooed animals are susceptible to the Rabies Virus. The infection is transmitted through direct contact of the virus in the blood stream of another animal or human. This can occur through wounds caused by bites and skin abrasions. But also for many animals by eating the flesh of an infected animal, during intercouse, or tissue transplantation, such as corneal transplants in humans.
Although it is possible for a ferret to contract rabies, as it is for any warm blooded mammal, the chance is extremely remote. Research studies have determined that ferrets are not susceptible to rabies virus through ingestion. There has never been a transmission of Rabies from a ferret to a human or to another animal. To date, less than 50 cases of documented Rabies in Ferrets have been recorded in the United States. This is in contrast to the hundreds of cats, dogs, and agricultural animals each year in the US.
In the United States, Rabies infection is one of there rarest infectious diseases reported in humans, and it is equally reare in domestic ferrets.
Rabies can be prevented through proper immunization with the USDA-licensed Rabies Virus Vaccine. As of Feb 2017 there are now three rabies vaccines that are USDA-licensed for use in ferrets: IMRAB®-3 (Manufacturer: Merial) and DEFENSOR®-1 and DEFENSOR®-3 (Manufacturer: Zoetis). These vaccines are produced from inactivated (killed) virus), and are the same vaccine products that are also approved for dogs, cats, horses, cattle, and sheep. Due to the fact that the manufacturers did not submit data on ferrets for greater than a year, all current labeled schedules for rabies vaccination of ferrets is annual immunization.
All warm-blooed animals are susceptible to the Rabies Virus. The infection is transmitted through direct contact of the virus in the blood stream of another animal or human. This can occur through wounds caused by bites and skin abrasions. But also for many animals by eating the flesh of an infected animal, during intercouse, or tissue transplantation, such as corneal transplants in humans.
Although it is possible for a ferret to contract rabies, as it is for any warm blooded mammal, the chance is extremely remote. Research studies have determined that ferrets are not susceptible to rabies virus through ingestion. There has never been a transmission of Rabies from a ferret to a human or to another animal. To date, less than 50 cases of documented Rabies in Ferrets have been recorded in the United States. This is in contrast to the hundreds of cats, dogs, and agricultural animals each year in the US.
In the United States, Rabies infection is one of there rarest infectious diseases reported in humans, and it is equally reare in domestic ferrets.
Rabies can be prevented through proper immunization with the USDA-licensed Rabies Virus Vaccine. As of Feb 2017 there are now three rabies vaccines that are USDA-licensed for use in ferrets: IMRAB®-3 (Manufacturer: Merial) and DEFENSOR®-1 and DEFENSOR®-3 (Manufacturer: Zoetis). These vaccines are produced from inactivated (killed) virus), and are the same vaccine products that are also approved for dogs, cats, horses, cattle, and sheep. Due to the fact that the manufacturers did not submit data on ferrets for greater than a year, all current labeled schedules for rabies vaccination of ferrets is annual immunization.